√100以上 e^x^2 969938-E x 2+1
Graph e^ (x^2) e−x2 e x 2 Find where the expression e−x2 e x 2 is undefined The domain of the expression is all real numbers except where the expression is undefined In this case, there is no real number that makes the expression undefined The vertical asymptotes occur at areas of infinite discontinuity No Vertical AsymptotesNow, we need to take some derivatives Let's go to n = 4 f (0)(x) = f (x) = ex2 f '(x) = ex2 ⋅ 2x f ''(x) = ex2 ⋅ 2 2x ⋅ ex2 ⋅ 2x = ex2(4x2 2) f '''(x) = 2ex2 ⋅ 2x ex2 ⋅ 8x 4x2 ⋅ ex2 ⋅ 2x = 4xex2 8xex2 8x3ex2Derivative of x^(2)*e^2 Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework
Integral E X 2 Dx Chegg Com
E x 2+1
E x 2+1-The partition theorem says that if Bn is a partition of the sample space then EX = X n EXjBnP(Bn) Now suppose that X and Y are discrete RV's If y is in the range of Y then Y = y is a event with nonzero probability, so we can use it as the B in the aboveThe first limit of the function is almost in the form of lim x → 0 e x − 1 x In this case, the exponential function and denominator contains x 2 but limit value is x tends to 0 So, it should be changed to apply this rule If x → 0, then x 2 → ( 0) 2 Therefore, x 2 → 0 The second function is almost same as the lim x → 0 sin




Graphs And Level Curves
Get an answer for '((e^x)(e^x))/2=1' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesThe expected value is also known as the expectation, mathematical expectation, mean, average, or first moment Expected value is a key concept in economics, finance, and many other subjects By definition, the expected value of a constant random variable X = c {\displaystyle X=c} is c {\displaystyle c} That's how $\mathsf E(X^2)$ (called the "second raw moment") relates to variance (called the "second central moment") Share Cite Follow edited Nov 9 '16 at 230 answered Nov 9 '16 at 223 Graham Kemp Graham Kemp 114k 6 6 gold badges 45 45 silver badges 103 103 bronze badges $\endgroup$ Add a comment
E−λ = λ The easiest way to get the variance is to first calculate EX(X −1), because this will let us useAs others have said, the result was correct but you took the long way to get there Where could you have saved time u = e^x 2 is a good substitution du = e^x dx here you could have saved a fewFree math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor
Prove that E (x E(x))^2 = E (x^2) – (E (x))^2 This problem is for a finance class Connect with a professional writer in 5 simple steps Please provide as many details about your writing struggle as possible Academic level of your paper Type of Paper Essay (Any 85 2 HallsofIvy said His point, about the limits of integration, was that it is well known that tex\int_ {\infty}^ {\infty} e^ {x^2}dx= 2\sqrt {\pi} /itex while the antiderivative is not an elementary function in other words, he could, theoretically, do it as a definite integral with the right limits but not as an indefinite integral2*X*e^ (x^2) The usual differentiation of e^x is e^x, this is the formula we'll use here As the term to be differentiated is e^ (x^2) On differentiating it would be e^ (x^2) * (differentiation of x^2) Differentiation of x^2 is 2x So the answer is 2x*e^ (x^2) Edit I'm sry I didn't see that



Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 325 Notes Ch3annotated Pdf



The Solution Curve Of The Differential Equation 1 E X 1 Y 2 Dy Dx Y 2 Which Passes Through The Point 0 1 Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, musicSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more




Question Video The Formula For Calculating The Variance Of A Discrete Random Variable Nagwa




1 Prove That E X E X E X E X 2 Prove That Chegg Com
答案解析 这是一个数学统计的问题 D (X)指方差,E(x)指期望 E (X)说简单点就是平均值,具体做法是求和然后除以数量 D (X)就是个体偏离期望的差,再对这个差值进行的平方,最后求这些平方的期望具体操作是,(个体期望),然后平方,再对这些平方值求平均值 说 To compute the variance you must also compute the second term in itex Var(X) = E(X^2) E(X)^2 /itex (which is a correct formula) The second term is the square of the expected value of itex X /itex It wouldn't be that way because what you called the professors way didn't say to multiply the probabilities times the X valuesV(X) = E(X )2 = E(X 2)− 2 = x In the discrete case, this is equivalent to = =∑ − All X V(X) σ2 (x µ)2 P(x) E Standard deviation of X The standard deviation is the positive square root of the variance, ie SD(X) =σ= σ2 Expectations Page 1




Gaussian Integral Wikipedia



Integral Xe X Dx Integral X 2 E X Dx Integral Ln X Chegg Com
The Gaussian integral, also known as the Euler–Poisson integral, is the integral of the Gaussian function f ( x ) = e − x 2 {\displaystyle f (x)=e^ {x^ {2}}} over the entire real line Named after the German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss, the integral isThe Derivative Calculator lets you calculate derivatives of functions online — for free!The function mathy=e^{x^2}/math should be familiar to you It defines the normal or gaussian distribution function This is what its curve looks like There is no known function which has a derivative equal to mathe^{x^2}/math In other




What Is The Graph Of E X Quora



Search Q Integration Formulas Tbm Isch
The expected value (or mean) of X, where X is a discrete random variable, is a weighted average of the possible values that X can take, each value being weighted according to the probability of that event occurring The expected value of X is usually written as E(X) or m E(X) = S x P(X = x) So the expected value is the sum of (each of the possible outcomes) × (the probability of theA Wikipedia page on Gaussian Functions states that ∫ − ∞ ∞ e − x 2 d x = π This is from infinity to infinity If the function can be integrated within these bounds, I'm unsure why it can't be integrated with respect to ( a, b) Is there really no way to find the integral of e − x 2, or are the methods to finding it found inMove slider below to add more terms 3




Gaussian Integral Wikipedia




Suppose E X 2 And E X X 1 27 5 A What Is E X2 Chegg Com
The Integral Calculator lets you calculate integrals and antiderivatives of functions online — for free!= λ X∞ k=1 λ λk−1 (k −1)! 微積分e^{x^2}的積分值(或稱高斯積分) 由 Issac 撰寫 , posted in 重積分與其應用 本篇主要想討論 的計算。
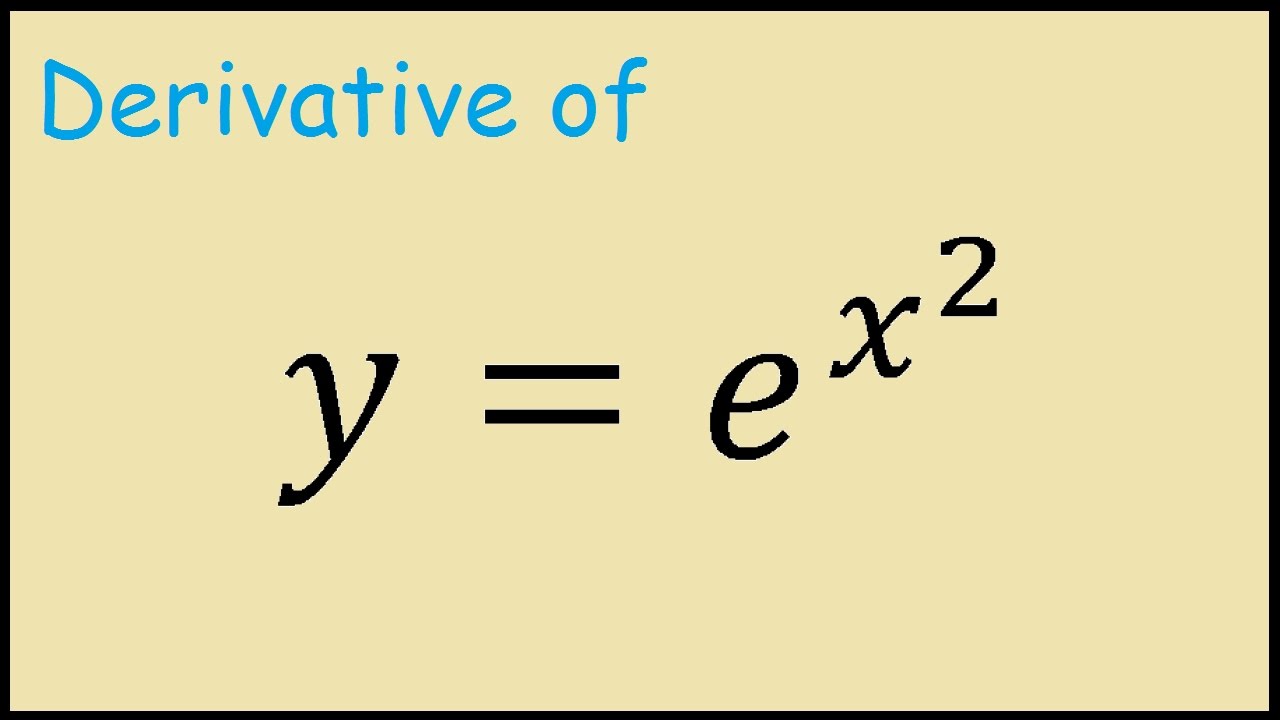



Derivative Of Y E X 2 Youtube




Integration By Parts
Integrate e^x^2 Natural Language;E−λ = λ X∞ k=0 λk k!Our calculator allows you to check your solutions to calculus exercises It helps you practice by showing you the full working (step by step integration) All common integration techniques and even special functions are supported



Www Math Uh Edu Jiwenhe Math1432 Lectures Lecture04 Handout Pdf




Ppt X Y 2 X 2 Y 2 2 Xy E X Y 2 E X 2 E Y 2 2 E Xy Powerpoint Presentation Id
I think you need to solve this equation numerically Specifically, we search search for the zeros of math f(x) = e^x e^{(x^2)} 2 e^{(x^4)}/math The plot below suggests that the only real solutions are mathx \in \{0, 1\}/math It's easy举报 x^2*e^ (x^2)dx = (x/2)d (e^ (x^2))由上式用"分部积分公式",得到前面一部分是 (x/2)* (e^ (x^2))l上面正无穷,下面负无穷,这一项的值为零,后面一部分还是一个反常(广义)积分,就是积分 (1/2)e^ (x^2)dx,从负无穷到正无穷这一部分需要用到二重积分,不能直接计算,我们 Using numerical methods, the area under the curve of e^x^2 is very close to about 6 iterations of the termbyterm integration of the series An approximation with this particular function where the terms increase for real itexx /tex, makes any




Ex 7 2 Integrate E 2x E 2x E 2x E 2x Ex 7 2



Graphing The Natural Exponential Function Y E X Youtube
Random Variability For any random variable X , the variance of X is the expected value of the squared difference between X and its expected value VarX = E(XEX)2 = EX2 (EX)2 (The second equation is the result of a bit of algebra E(XEX)2 = EX2 2⋅X⋅EX (EX)2 = EX2 2⋅EX⋅EX (EX)2)Variance comes in squared units (and adding a constant to aPlot x e^x, x^2 e^x, x=0 to 8 WolframAlpha Rocket science?Not a problem Unlock StepbyStep Extended Keyboard
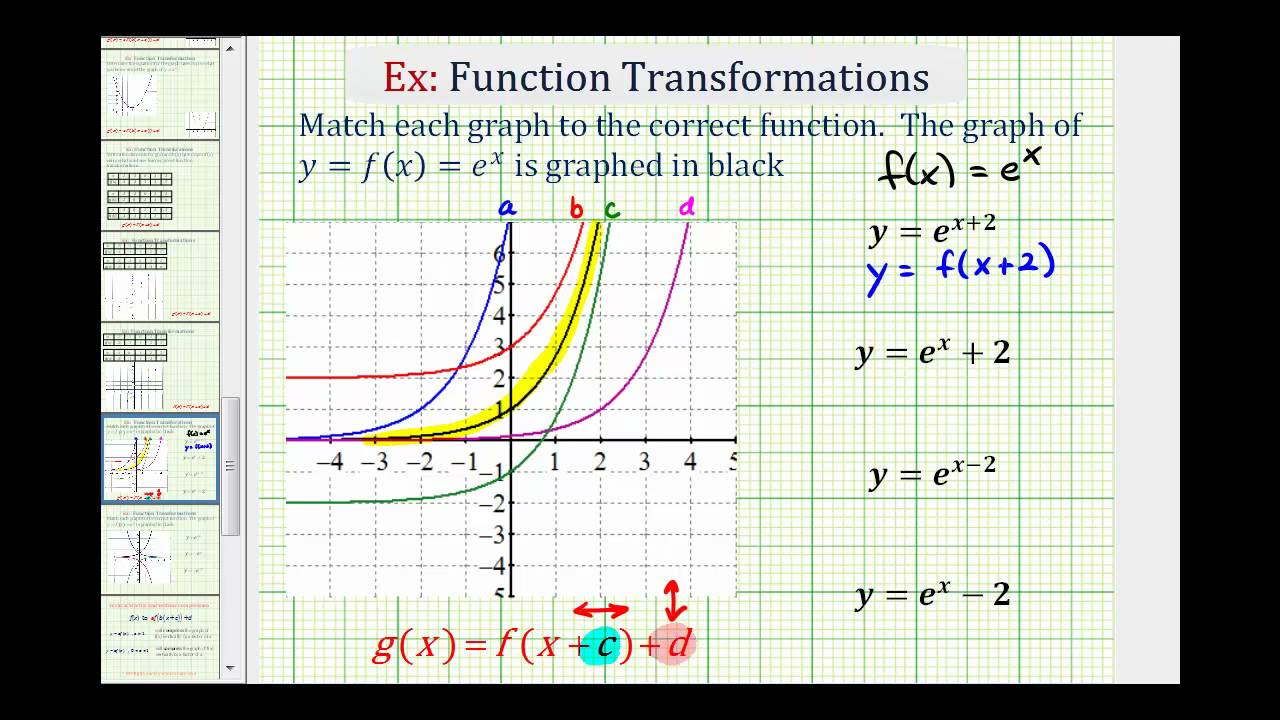



Horizontal And Vertical Translations Of Exponential Functions College Algebra
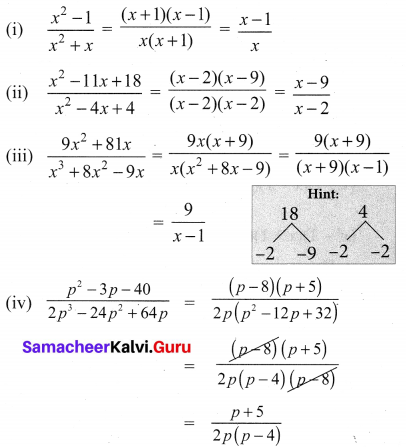



Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3 4 Samacheer Kalvi
미분 계산기 우측의 도함수 exp (x^2) to x = 2*x*%e^x^2 단계별 풀이 보이기 그래프 보기 식 바꾸기 이 페이지에 직접 링크 derivati ve_help 구문 규칙 표시 Because e^x^2 is a function which is a combination of e x and x 2, it means we can perform the differentiation of e to the x 2 by making use of the chain rule Using the chain rule to find the derivative of e^x^2 Although the function e x 2 contains no parenthesis, we can still view it as a composite function (a function of a function)Our calculator allows you to check your solutions to calculus exercises It helps you practice by showing you the full working (step by step differentiation) The Derivative Calculator supports computing first, second, , fifth derivatives as well as



Integrating E X 2 The Gaussian Integral Youtube



Integrate Xe X 1 X 2 Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queries Students (upto class 102) preparing for All Government Exams, CBSE Board Exam, ICSE Board Exam, State Board Exam, JEE (MainsAdvance) and NEET can ask questions from any subject and get quick answers by #int_0^1 e^(x^2)dx = 1/42 1/10 1/3 1 ~~1457# A calculator should give an approximation of #1463# , so our answer isn't too terrible Increasing the number of terms of the maclaurin series in the application will make the approximation more preciseIntegral of e^ {x^2} \square!




How To Solve This Question Integral E X X 2 1 X 1 2 Quora
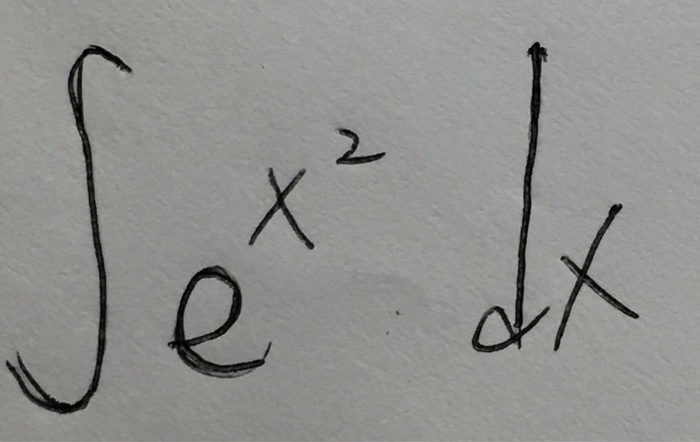



Integral E X 2 Dx Chegg Com
公式5について,期待値の場合は定数倍は外に出ましたが,分散は定義に (x i − μ X) 2 (x_i\mu_X)^2 (x i − μ X ) 2 という二乗の式が含まれているので外にだすときに二乗がかかります。; 分散V (X)の定義とE 分散・標準偏差は基本的に「 データの分析(2) 」で扱っている『データの分散・標準偏差』と同じ考え方で求めることができます。 すなわち、各確率から期待値(平均値)を引いたものの2乗をk=1~nまで総和すれば良いのです。 また Hence, the Maclaurin series formula is N ∑ n=0 f (n)(0) n!
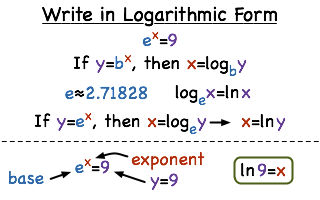



How Do You Convert From Exponential Form To Natural Logarithmic Form Printable Summary Virtual Nerd




What Is The Derivative Of Math E X 2 Math Quora
Substitution integral of (e^x)/ (e^xe^ {x)}, u=e^x \square! E(X^2) 是 X^2 的期望 比如,P{X=1} = 2/3, P{X=0} = 1/6, P{X=1} = 1/6 EX = 1 * 2/3 0 * 1/6Fortunately, there is a clever trick that will allow us to calculate the value even without looking for a primitive function, and that's what we will do for the rest of this article First, let's denote I = ∫_ {∞}^∞ e^ {x^2}\,dx\, Obviously, changing the letter denoting the variable will not




What Is The Expected Value Of The Expected Of X Conditional Of Y E E X Y And Also If Possible E X 2 Y Cross Validated




Evaluate The Indefinite Integral Integral E X Dx Chegg Com
Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!1 Answer1 Based on the comments, I assume the that the X in part 1 and 2 is the same Then we know E X = 1, V a r ( X) = 4 You may now find the answer by using the relationship V a r ( X) = E X 2 − ( E X) 2 ( Hint The correct answer is 41) I leave the below as an example of why the information in the first part is not sufficient




Ex 7 9 15 Direct Integrate X Ex 2 Dx From 0 To 1 Teachoo



What Is The Derivative Of Log E X X 2 X 2 3 4 Wrt X Quora




How To Solve X 2 E X Mathematics Stack Exchange



Solve The Differential Equations D 2 2d 1 Y X 2 Ex Sin X 2x Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
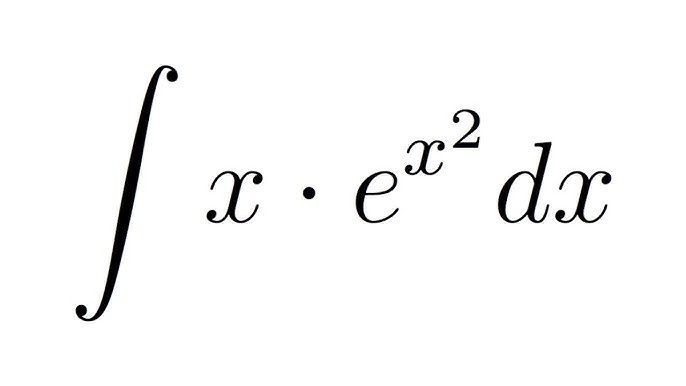



Method 2 Integral Of X E X 2 Substitution Youtube




The Value Of The Integral Overset 1 Underset 0 Int E X 2 Dx Lies In The Integral
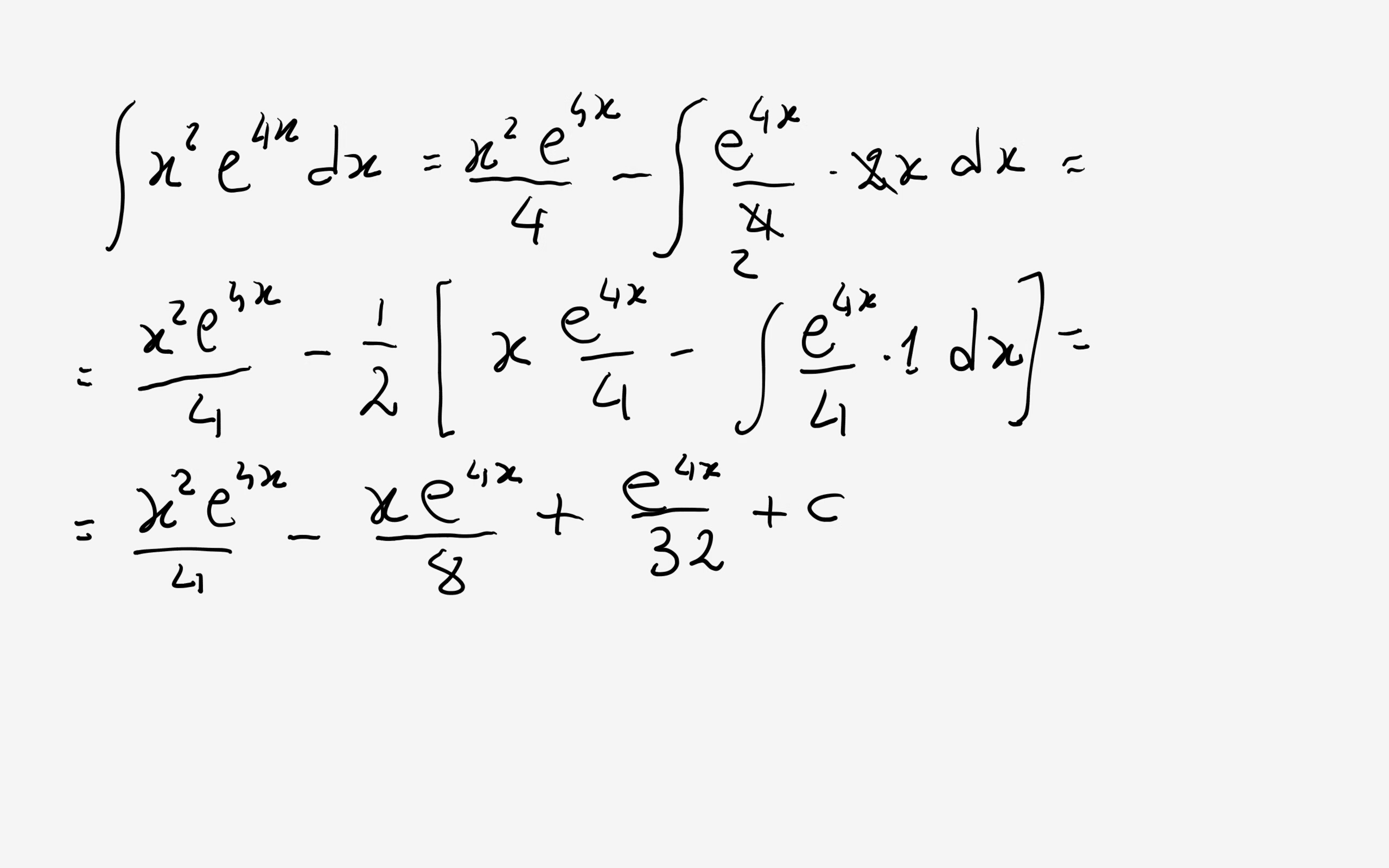



How Do You Integrate X 2 E 4x Dx Socratic




Ex 7 3 24 Integration Ex 1 X Cos2 Ex X Dx Equals




Variance Wikipedia




Ex 7 10 8 Evaluate Integral 1 X 1 2x2 E2x Dx Ex 7 10




Ex 7 6 24 Integrate E X Sec X 1 Tan X Dx Is A E X Cos X
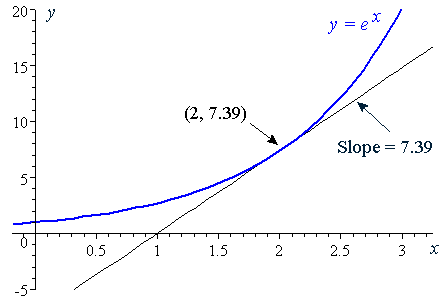



6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function




Ex 2 Manual Ko Propo




Evaluate The Double Integral Of Exp X 2 Y 2 Where The Solid Is The Half Circle Given By X 2 Y 2 4 And X Y 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



What Is The Antiderivative Of Math E X 2 Math Quora
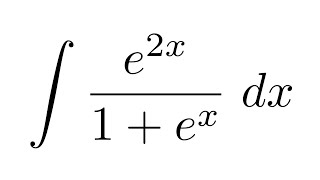



Integral Of E 2x 1 E X Substitution Youtube




Ncert Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 7 Integers Ex 7 5




What Is The Expected Value Of The Expected Of X Conditional Of Y E E X Y And Also If Possible E X 2 Y Cross Validated




What Is The Integral Math Int X 2 E X 2 Dx Math Quora




How To Calculate Indefinite Integral Of Math E X 2 Math Quora




If F X E X E X 2 Then Inverse Of F X Is




What Is An Antiderivative For E X 2 Week 10 Lecture 8 Mooculus Youtube
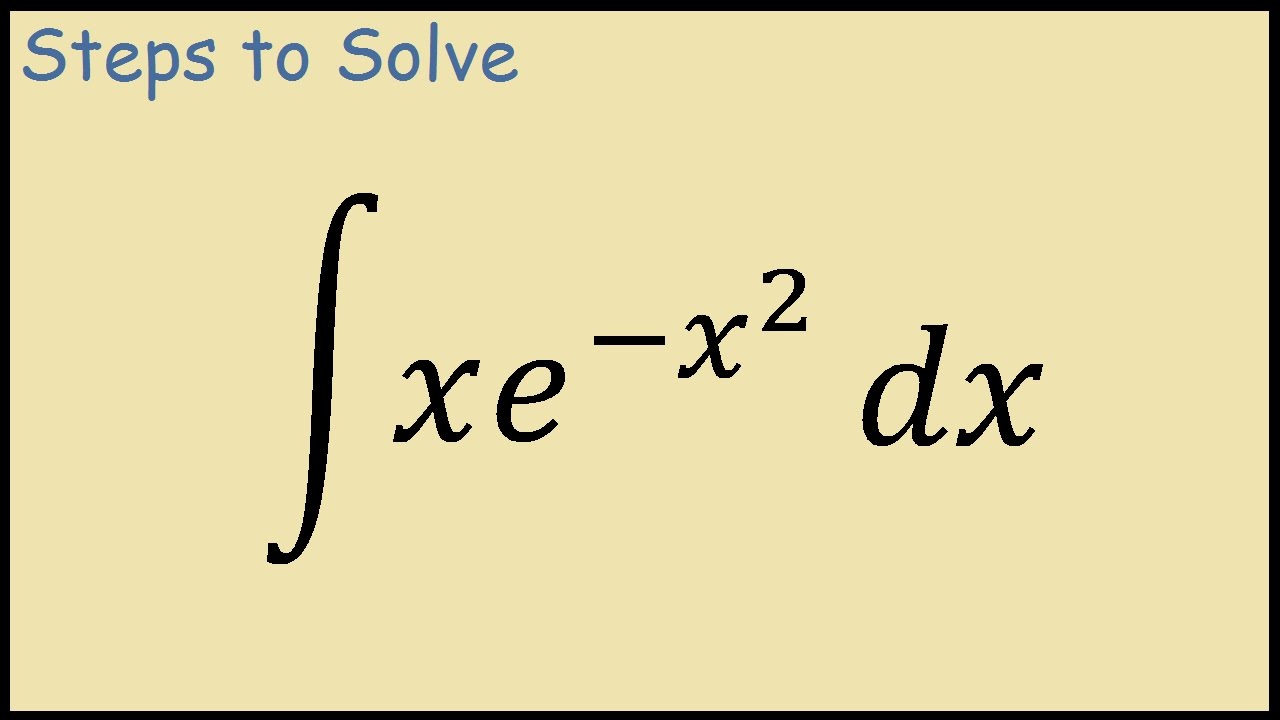



How To Integrate Xe X 2 Youtube




Taylor Series Expansions Of Exponential Functions



Derivative Of E X Calculating Derivatives Of Exponential Functions



Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 325 Notes Ch3annotated Pdf



Graphs E X And Ln X Geogebra



File E X 2 Jpg Wikipedia




Integrate E Tan 1x 1 X X 2 1 X 2 Dx Brainly In




What Is The Antiderivative Of E X 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Differentiate E X 2 Tan 1 X Sqrt 1 X 2 W R T X



Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 325 Notes Ch3annotated Pdf




Graphs And Level Curves




Exponential Function Wikipedia




Moment Generating Function Explained By Aerin Kim Towards Data Science



Test The Improper Integral E X2 For Convergence Stumbling Robot



3
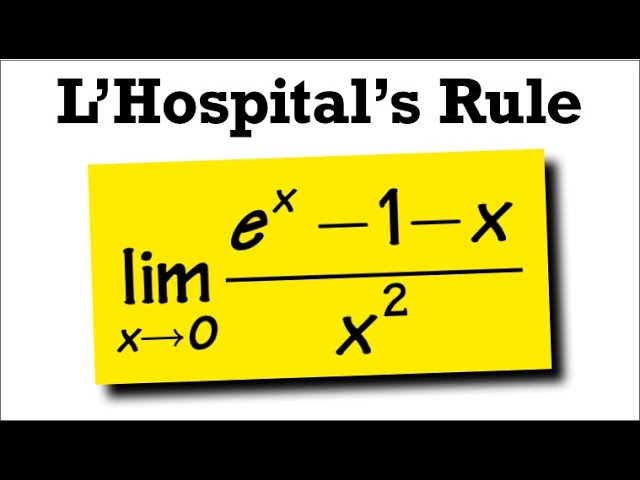



Limit Of E X 1 X X 2 As X Goes To 0 L Hospital S Rule Youtube




If Y Ex Sin X Prove That D2y Dx2 2 Dy Dx 2y 0 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com 5p09j033
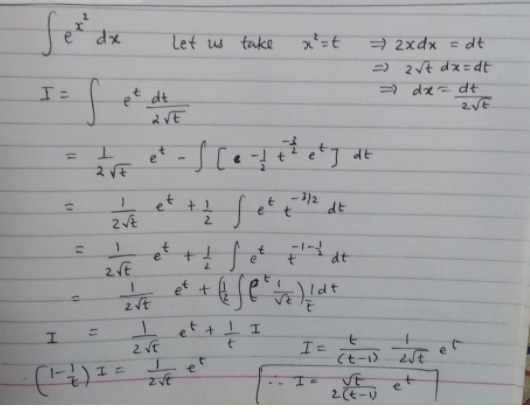



Integral E X 2 Dx Wegglab




Misc 8 Integrate E5 Log X E4 Log X Log X E2 Log X




Gaussian Integral Wikipedia




Variance Wikipedia




Maclaurin Series Of Eˣ Video Khan Academy




How To Integrate Xe X Steps Tutorial Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Find E X 2 E X 4 E 2x Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




My Cloud Expert Series Ex2 Ultra Western Digital Store



Parts Ex 2




Ex 7 6 19 Integrate Ex 1 X 1 X2 Class 12 Cbse Ex 7 6



E Calculator Eˣ E Raised To Power Of X




19 Sum Of The Two Integral Int E X 5 2 D X 3 Int 0 2 3 E 9 X 2 3 2 D X Is
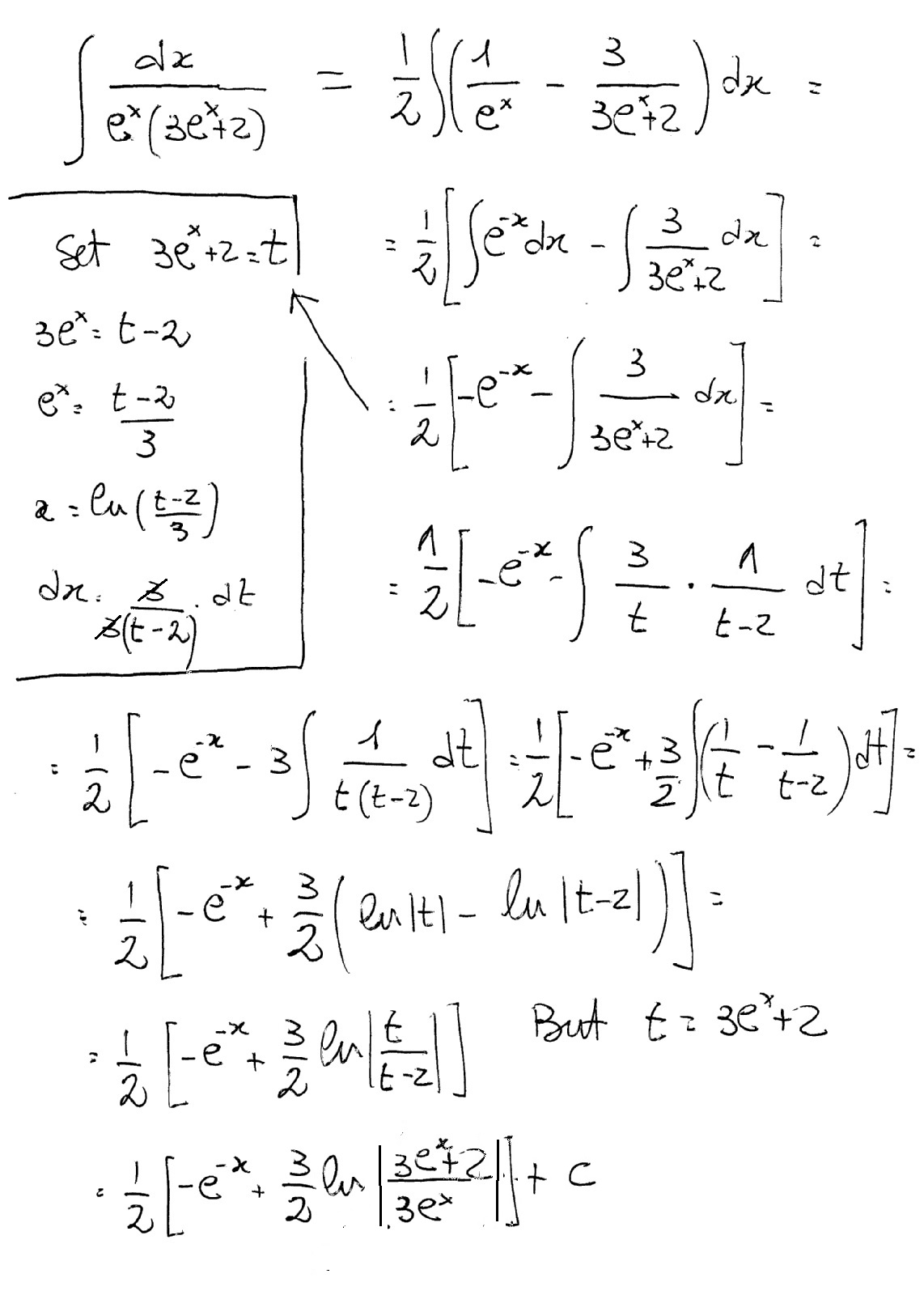



How Do You Evaluate The Integral Of Dx E X 3e X 2 Socratic




Verify The Given Function Including The Integral E X 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Ex 7 3 24 Integration Ex 1 X Cos2 Ex X Dx Equals
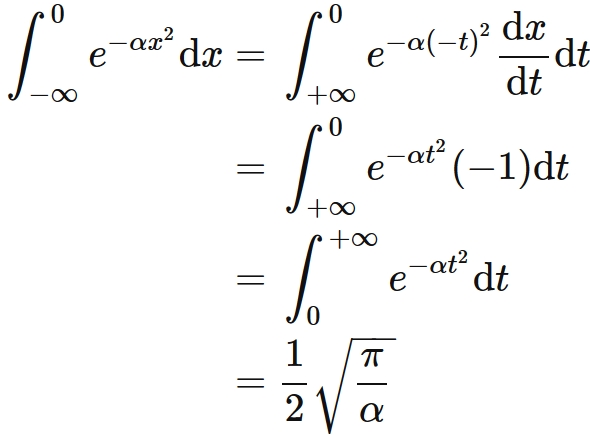



41 E X 2 Png




Solve Dy Dx 2y E X



Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 325 Notes Ch3annotated Pdf
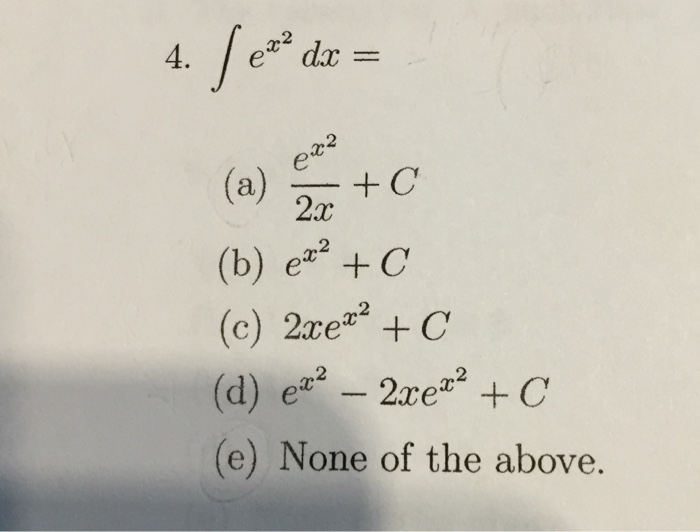



Integral E X 2 Dx E X 2 2x C E X 2 C 2xe X 2 Chegg Com




Differentiation Of Exponential And Logarithmic Functions



1




Misc 41 Class 12 Integration Dx Ex E X Is Equal
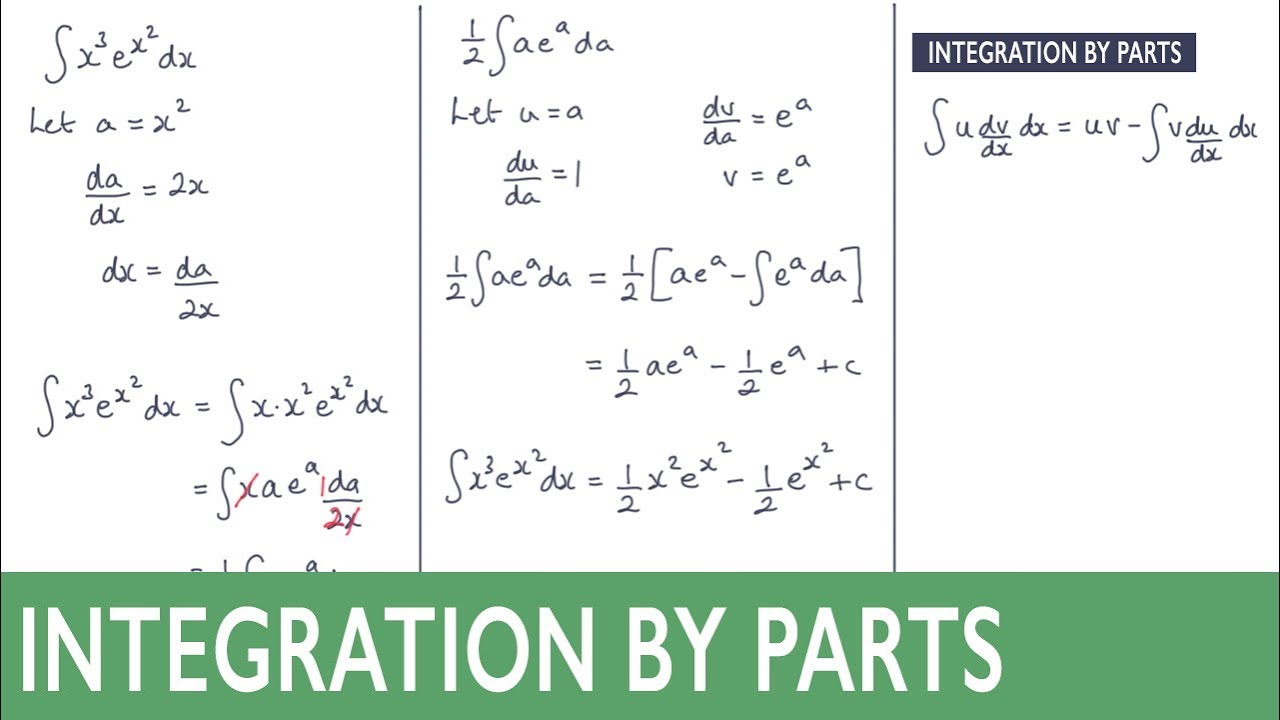



How To Integrate X 3 E X 2 Using Integration By Parts Youtube



Integral Of E 2x




Integral Of The Type E X F X F X Dx Integration Rules Solved Examples




Ac The Second Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus




Cosh X Function Is The Average Of E X And E X Hyperbolic Functions Download Scientific Diagram




8 6 Natural Logarithms Ppt Download
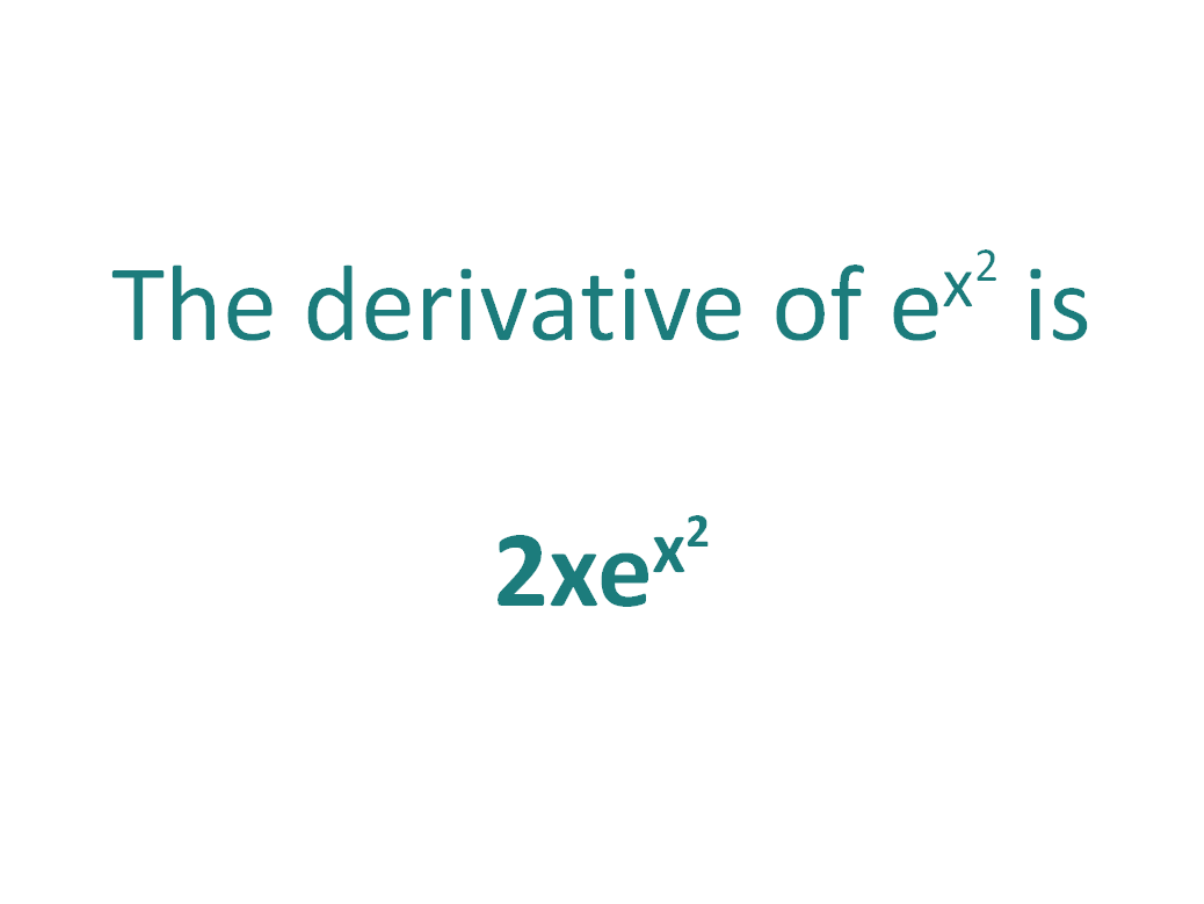



The Derivative Of E X 2 Derivativeit
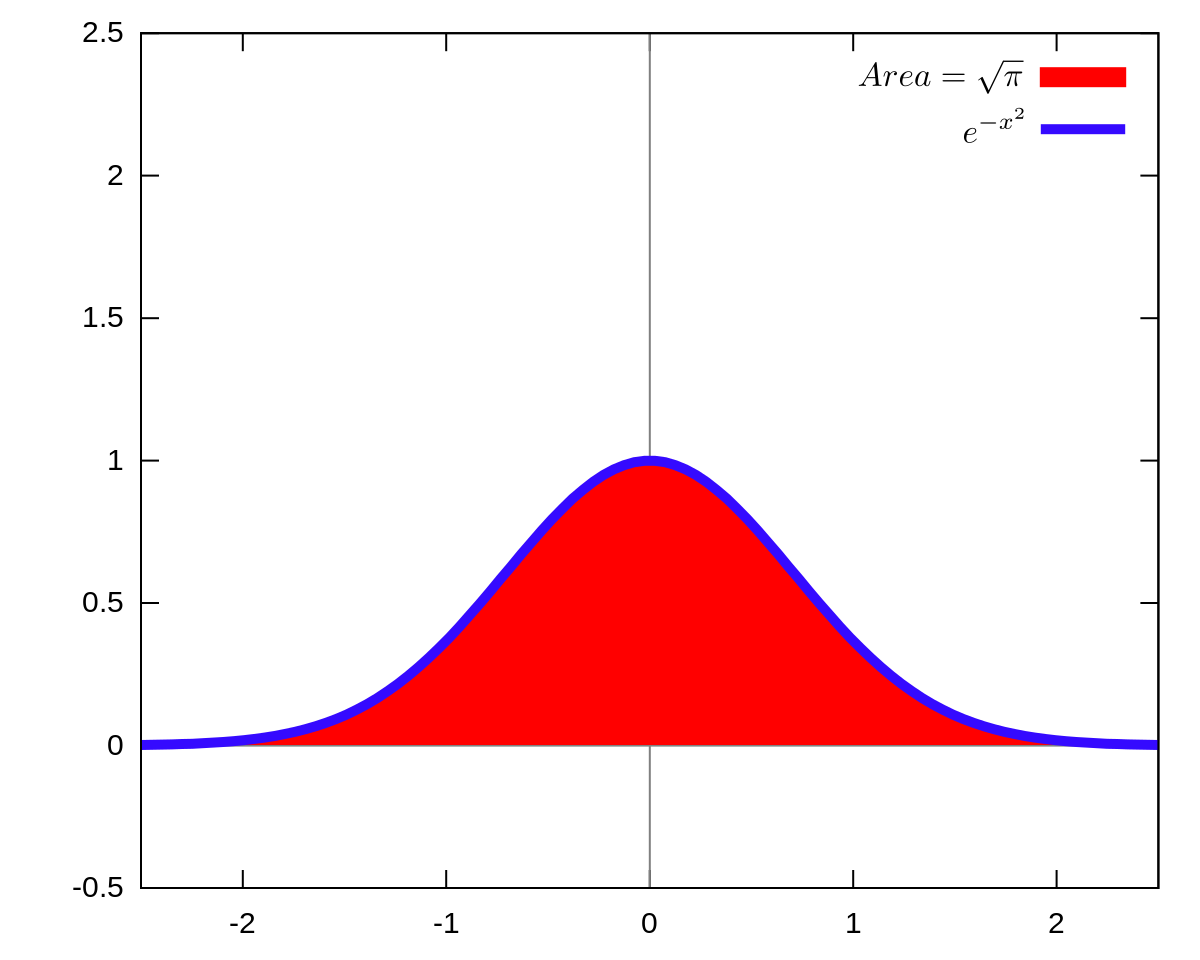



Gaussian Integral Wikipedia




Ex 7 6 3 Integrate X 2 E X Chapter 7 Class 12 Ncert
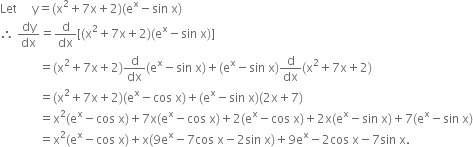



Differentiate X2 7 X 2 Ex Sin X W R T X Zigya




5 6 Integrals Involving Exponential And Logarithmic Functions Mathematics Libretexts



The Improper Integral Of E X From 0 To Infinity Youtube




Gaussian Integral Wikipedia



How To Solve Math X 2 Displaystyle Frac D 2y Dx 2 4x Displaystyle Frac Dy Dx 2y E X Math Quora



Variance 11 10




Ex 6 2 19 The Interval In Which Y X2 E X Is Increasing
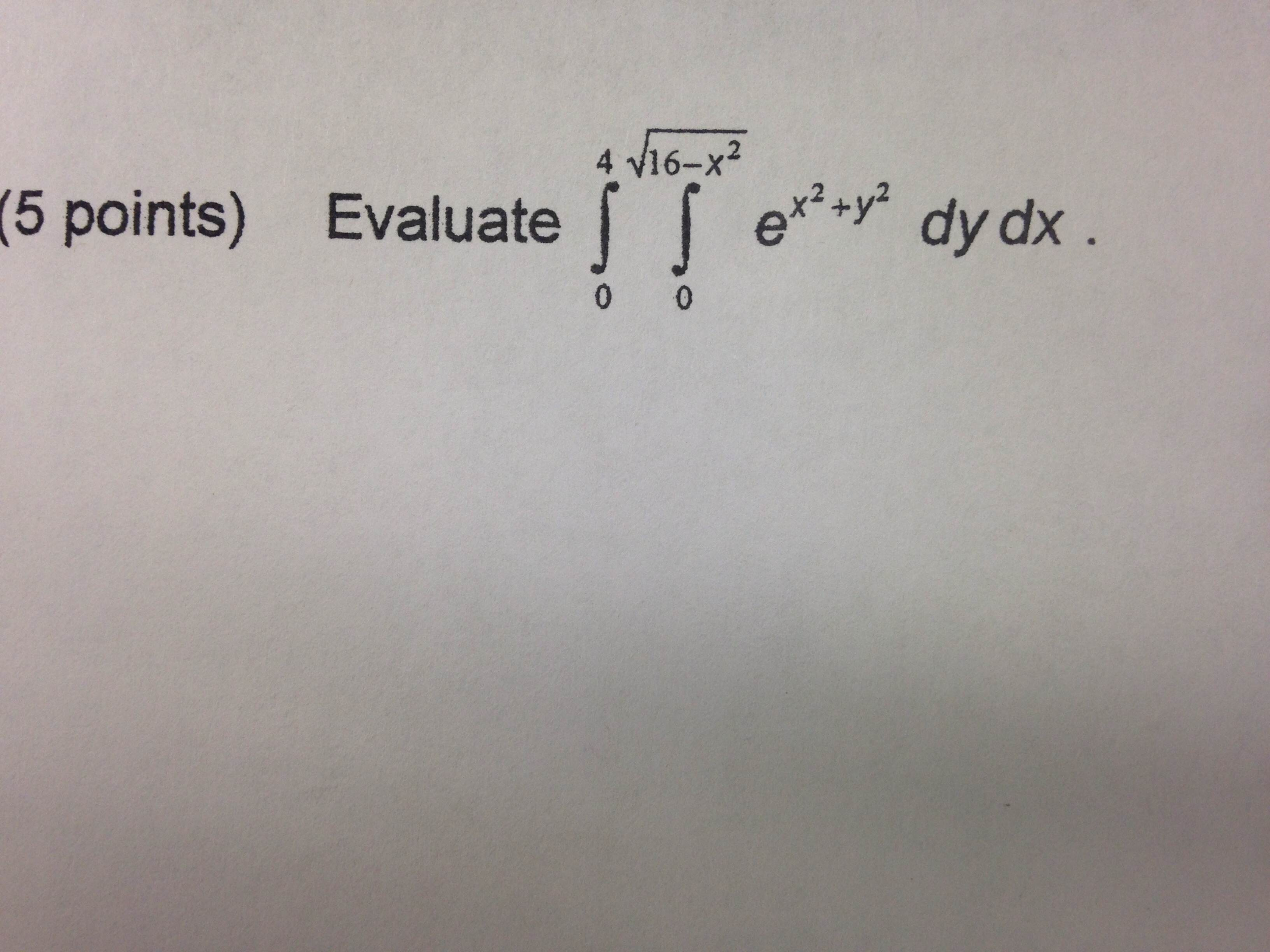



Evaluate Double Integrate E X 2 Y 2 Dydx Chegg Com


コメント
コメントを投稿